Cable shielding materials are an essential component in […]
Cable shielding materials are an essential component in electronic systems, protecting cables from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).
Braided shielding: Braided shielding consists of a woven mesh of copper or other conductive materials that are wrapped around the cable. Braided shielding is flexible and easy to install, making it a popular choice for many applications. It is also effective at reducing EMI and RFI, making it suitable for high-performance systems.
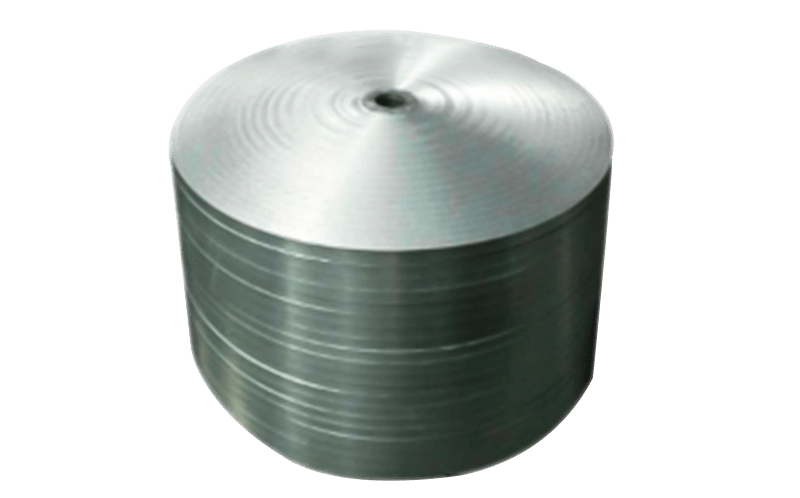
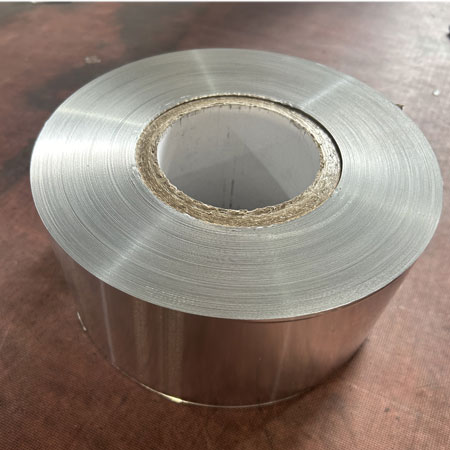
Foil shielding: Foil shielding consists of a thin layer of aluminum or copper foil that is wrapped around the cable. Foil shielding is lightweight and easy to install, making it suitable for applications where space is limited. It is also effective at reducing EMI and RFI, making it suitable for many electronic systems.
Spiral shielding: Spiral shielding consists of a helical wrap of conductive material that is wrapped around the cable. Spiral shielding is flexible and easy to install, making it suitable for many applications. It is also effective at reducing EMI and RFI, making it suitable for high-performance systems.
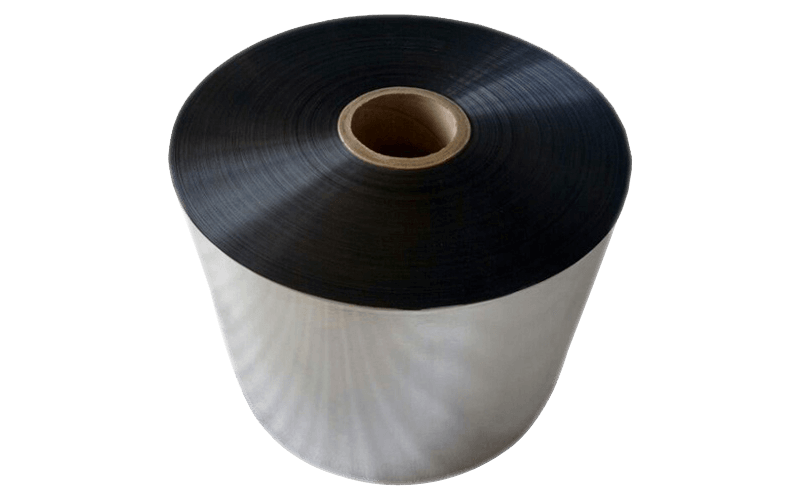
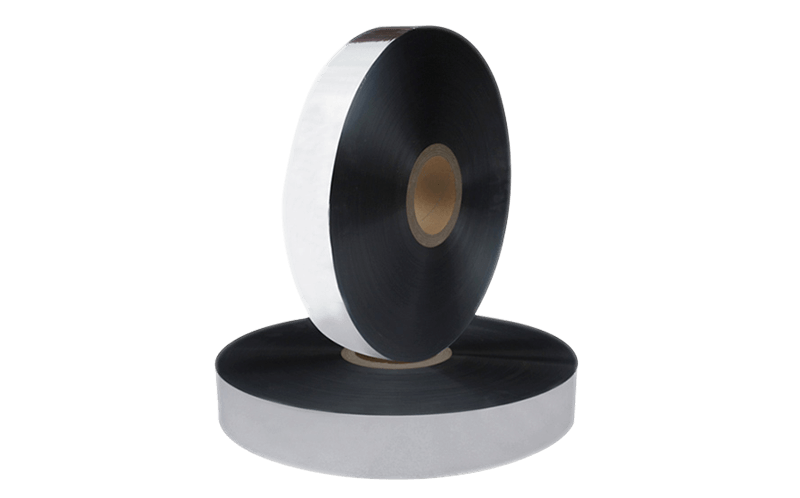
Combination shielding: Combination shielding consists of two or more types of shielding materials combined to provide additional protection against EMI and RFI. For example, a cable may have a layer of braided shielding over a layer of foil shielding.
Each type of cable shielding material has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, braided shielding is flexible and easy to install but can be heavy and bulky. Foil shielding is lightweight and easy to install but can be less flexible than other types of shielding. Spiral shielding is flexible and easy to install but can be less effective at reducing EMI and RFI than other types of shielding.
Choosing the right cable shielding material depends on the specific needs of the electronic system. Factors such as the level of EMI and RFI present, the space available for the cable, and the level of flexibility required will all impact the choice of shielding material. By selecting the appropriate shielding material for each application, engineers can ensure the safe and efficient operation of electronic systems, reducing the risk of signal interference and improving overall performance.